Simulation Study on the tunnel networks of subterranean termites and the foraging behavior
Sang-Hee Lee; Nan-Yao Su
|
Journal of Asia-Pacific Entomology
13
(2010)
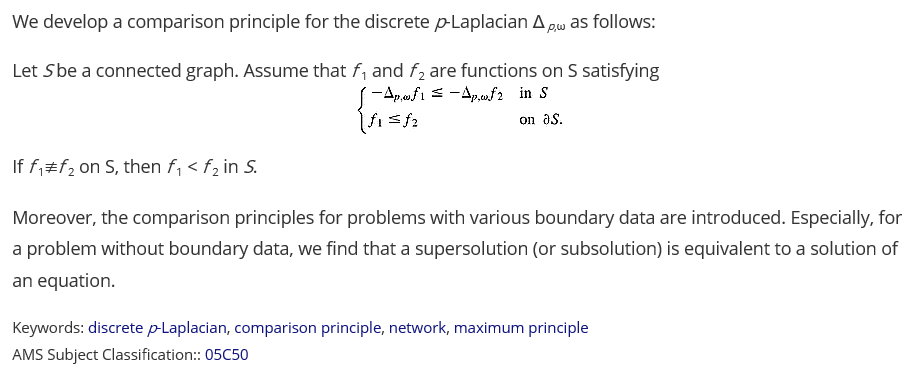
Most subterranean termites forage for food by creating tunnel galleries underground. These tunnel networks reflect a compromise between foraging efficiency and other environmental constraints, such as soil hardness and moisture content. Thus, understanding tunnel networks is important for understanding foraging behavior. Due to the difficulties in direct observation of tunneling patterns in the field, we used a theoretical approach for this analysis. We first constructed a lattice model to simulate the tunnel networks of Coptotermes formosanus Shiraki and Reticulitermes flavipes (Kollar) on the basis of the experimental data provided by Su et al. (Su, N.-Y., Stith, B.M., Puche, H., Bardunias, P., 2004. Characterization of tunneling geometry of subterranean termites (Isoptera: Rhinotermitidae) by computer simulation. Sociobiology 44 (3), 471–483.). Using this model and two of its modified versions, we explored the relationship between the food encounter rate and food distributions and analyzed how this relationship is influenced by changes in the tunnel characteristic constituents, such as the branching tunnel length and frequency. Additionally, we investigated the effects of landscape heterogeneity on the foraging efficiency. In the discussion, we briefly introduced our novel individual-based model comprising individual termites and their surroundings, and we addressed the necessity of this model in the functioning of the network and the formation of the network in relation to foraging behavior.
- 초록
Most subterranean termites forage for food by creating tunnel galleries underground. These tunnel networks reflect a compromise between foraging efficiency and other environmental constraints, such as soil hardness and moisture content. Thus, understanding tunnel networks is important for understanding foraging behavior. Due to the difficulties in direct observation of tunneling patterns in the field, we used a theoretical approach for this analysis. We first constructed a lattice model to simulate the tunnel networks of Coptotermes formosanus Shiraki and Reticulitermes flavipes (Kollar) on the basis of the experimental data provided by Su et al. (Su, N.-Y., Stith, B.M., Puche, H., Bardunias, P., 2004. Characterization of tunneling geometry of subterranean termites (Isoptera: Rhinotermitidae) by computer simulation. Sociobiology 44 (3), 471–483.). Using this model and two of its modified versions, we explored the relationship between the food encounter rate and food distributions and analyzed how this relationship is influenced by changes in the tunnel characteristic constituents, such as the branching tunnel length and frequency. Additionally, we investigated the effects of landscape heterogeneity on the foraging efficiency. In the discussion, we briefly introduced our novel individual-based model comprising individual termites and their surroundings, and we addressed the necessity of this model in the functioning of the network and the formation of the network in relation to foraging behavior.
- 초록
Most subterranean termites forage for food by creating tunnel galleries underground. These tunnel networks reflect a compromise between foraging efficiency and other environmental constraints, such as soil hardness and moisture content. Thus, understanding tunnel networks is important for understanding foraging behavior. Due to the difficulties in direct observation of tunneling patterns in the field, we used a theoretical approach for this analysis. We first constructed a lattice model to simulate the tunnel networks of Coptotermes formosanus Shiraki and Reticulitermes flavipes (Kollar) on the basis of the experimental data provided by Su et al. (Su, N.-Y., Stith, B.M., Puche, H., Bardunias, P., 2004. Characterization of tunneling geometry of subterranean termites (Isoptera: Rhinotermitidae) by computer simulation. Sociobiology 44 (3), 471–483.). Using this model and two of its modified versions, we explored the relationship between the food encounter rate and food distributions and analyzed how this relationship is influenced by changes in the tunnel characteristic constituents, such as the branching tunnel length and frequency. Additionally, we investigated the effects of landscape heterogeneity on the foraging efficiency. In the discussion, we briefly introduced our novel individual-based model comprising individual termites and their surroundings, and we addressed the necessity of this model in the functioning of the network and the formation of the network in relation to foraging behavior.
More